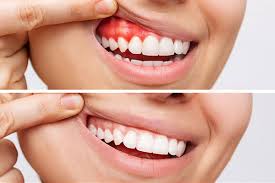
Signs of Gum Disease:
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding your teeth. It can range from mild inflammation (gingivitis) to more severe conditions that can result in tooth loss (periodontitis). Gum disease is often painless in its early stages, which is why it’s essential to be aware of the warning signs. Early detection and treatment can prevent the progression of gum disease and protect your overall oral health.
You Might Also Interested In: Contractor SEO Agency
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease is primarily caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If plaque is not removed regularly through brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can irritate and infect the gums. Other contributing factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and underlying health conditions such as diabetes.
The Two Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease develops in stages, each with its own symptoms:
- Gingivitis: This is the mildest form of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums. It’s usually caused by poor oral hygiene and can be reversed with proper care.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. This more severe stage affects the deeper tissues and bone that support the teeth, leading to tooth loss if not managed.
Early Signs of Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
The early signs of gum disease are often subtle but should not be ignored. Detecting these symptoms early can help prevent more serious complications. Key signs include:
- Red or Swollen Gums
Healthy gums are typically firm and pink. If you notice that your gums are red, swollen, or tender to the touch, it could be a sign of gingivitis. This inflammation occurs as a result of bacteria irritating the gum tissue. - Bleeding Gums
If your gums bleed easily when you brush or floss, it’s a common indication of gum disease. While occasional bleeding can occur from brushing too hard, persistent bleeding, especially during regular oral hygiene practices, is a red flag. - Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Chronic bad breath or a persistent bad taste in your mouth may be a result of bacteria buildup. When plaque and food particles are not properly removed, they can produce an unpleasant odor, which is often an early sign of gum disease. - Gum Sensitivity
In the early stages of gum disease, you may notice that your gums feel more sensitive, especially when eating or drinking. This could be due to inflammation and irritation caused by plaque along the gumline. - Gums Pulling Away from Teeth (Receding Gums)
If your gums appear to be pulling away from your teeth, exposing more of the tooth or its roots, it may be a sign of gum recession, which can be an early symptom of periodontal disease. Receding gums can make your teeth appear longer and increase sensitivity.
Advanced Signs of Gum Disease (Periodontitis)
If gum disease progresses to periodontitis, more severe symptoms can develop. These signs indicate that the infection is affecting the deeper tissues and bone structure:
- Persistent Bad Breath
Bad breath caused by gum disease can become more frequent and harder to mask as periodontitis sets in. The bacteria responsible for the infection continue to thrive and release foul-smelling gases. - Loose or Shifting Teeth
As periodontitis progresses, the supporting bone and tissues around your teeth weaken, causing your teeth to feel loose or even shift. This can lead to changes in your bite or the way your teeth fit together. - Pus Between Teeth and Gums
The presence of pus between your teeth and gums is a clear sign of infection. This discharge is a serious symptom of advanced gum disease and should be addressed by a dentist immediately. - Pain When Chewing
If you experience pain while chewing, it could be due to gum infection or bone loss around your teeth. This discomfort can range from mild to severe, depending on the progression of the disease. - Changes in Tooth Alignment
As the bone supporting your teeth deteriorates due to periodontitis, your teeth may begin to shift. This can lead to gaps between your teeth, changes in how they fit together, or even affect the fit of dental appliances such as dentures. - Gum Abscesses
An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms as a result of infection. Gum abscesses can cause significant pain, swelling, and discomfort and are a clear indication that the gum disease has progressed to a serious level.
Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing gum disease. These include:
- Smoking or using tobacco products: Tobacco use is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease and can interfere with successful treatment.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, leading to gum disease.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and other hormonal changes can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to infection.
- Chronic illnesses: Conditions like diabetes and autoimmune diseases can increase the risk of gum disease.
- Medications: Some medications, including those that reduce saliva flow, can contribute to gum disease by making the mouth dry and more prone to bacterial buildup.
Prevention and Treatment
The good news is that gum disease can be prevented and, in many cases, reversed if caught early. Here’s how to maintain healthy gums and prevent the onset of gum disease:
- Brush twice a day: Use fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean your teeth and gums effectively.
- Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline, areas that your toothbrush can’t reach.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential to catching gum disease early and preventing its progression.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and quitting can improve your gum health significantly.
- Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium, can help maintain healthy gums.
Conclusion
Recognizing the early signs of gum disease is crucial to preventing more severe oral health problems. If you notice any symptoms like swollen gums, bleeding, or bad breath, it’s important to see your dentist promptly for an evaluation. With proper care, including good oral hygiene and regular dental visits, you can prevent gum disease or stop it from worsening, ensuring a healthy smile for life.