Emergence of the Pet Economy
The commodification of animal companionship has become a defining feature of modern consumer behavior. Pet ownership, once considered a leisurely or sentimental pursuit, now constitutes a robust economic sector. Companion animals are no longer peripheral to households—they are central. This societal shift has precipitated an ecosystem of goods and services tailored to the perceived needs of pets. Among the most visible artifacts of this evolution is the pet toy.
Toys have assumed a utilitarian role in the pet economy, far removed from their previous categorization as novelty items. As disposable incomes rise and households invest more in their animals, pet toys are increasingly seen as essential tools for managing behavior, alleviating stress, and enhancing quality of life for companion animals.
For more info visit: https://market.us/report/pet-toys-market/
Pet Toys as Functional Commodities
Pet toys today are not primarily whimsical or decorative. Their designs are informed by behavioral psychology, veterinary science, and even child development principles. Products that once existed to entertain now serve to improve mental acuity, promote physical activity, or prevent destructive tendencies. The market is no longer driven purely by aesthetics or impulse purchases; it is governed by utility, research, and targeted outcomes. This transformation reflects an overarching reassessment of human obligations toward non-human cohabitants.
For more info visit: https://market.us/report/pet-toys-market/
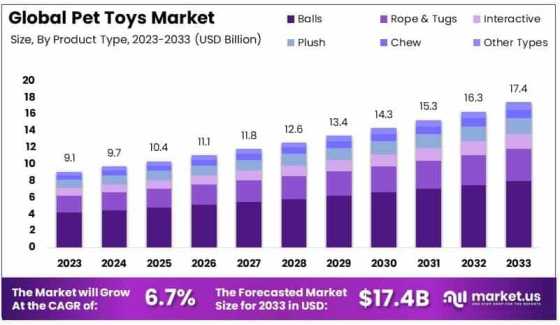
Market Composition and Classification
Segmentation by Product Type and Material
The pet toy market is functionally segmented into categories that correspond to a pet’s developmental or behavioral needs. Chew toys dominate among dogs, serving dual purposes: teething relief and anxiety reduction. Interactive toys, which may respond to touch or sound, engage a pet’s problem-solving instincts. Plush toys provide comfort and mimic companionship, while puzzles are designed to improve cognitive function.
Material choice is critical. Traditional plastic and rubber variants remain prevalent due to cost efficiency, but consumer demand for sustainability is driving the growth of toys made from natural rubber, recycled textiles, or biodegradable starch-based polymers. Toxicity concerns have pushed many manufacturers to adopt BPA-free, phthalate-free, and non-allergenic components. The selection of materials directly influences pricing, durability, and environmental impact.
Target Demographics: Species, Breed, and Behavior
Segmentation doesn’t end at product type. Today’s pet toy manufacturers design for specificity—based on species, breed, age, and behavioral profiles. A one-size-fits-all approach is no longer commercially viable. For example, a toy suitable for a small indoor cat will likely be ineffective or even hazardous for a high-energy Labrador retriever. Products are now engineered to match breed-specific chewing strength, instinctual drives, and cognitive capacity.
Behavioral targeting is particularly nuanced. Toys for highly anxious animals are often designed with textures or scents that promote calm. Conversely, high-energy pets require toys that provide extended physical engagement, such as automated fetch machines or climbing systems. These considerations elevate pet toys from generic merchandise to purpose-built instruments.
Operational and Economic Factors
Supply Chain Complexities and Manufacturing Trends
Pet toy manufacturing involves a multi-tiered supply chain subject to significant volatility. The cost and availability of raw materials—particularly silicone, fabric, and electronic components—can fluctuate based on global trade dynamics. Logistical delays and shipping costs have further complicated inventory management.
To counteract these challenges, many companies are moving toward nearshoring production or integrating vertically to regain control over their supply networks. Automation in manufacturing, such as injection molding and robotic assembly, is also becoming more common, particularly among large-scale producers.
Pricing Architecture and Retail Channel Shifts
The pricing of pet toys is dictated by a blend of production costs, brand positioning, and consumer psychology. Premium brands often charge a markup justified by perceived quality or eco-conscious materials. Meanwhile, value-oriented brands compete on volume and accessibility.
The retail landscape has shifted substantially. While traditional pet stores still play a role, e-commerce has taken precedence, particularly among younger consumers. Direct-to-consumer websites, online marketplaces, and subscription boxes have introduced new pricing strategies and purchasing behaviors. Data collected from digital platforms enables granular targeting and customized product offerings.
Prospects and Constraints
Technological Integration in Toy Design
The pet toy market is inching toward the domain of smart technology. Motion sensors, automated movement, and mobile app interfaces are now embedded in certain high-end toys. These features enable dynamic play, responsiveness, and tracking of usage metrics. Though adoption remains limited by price sensitivity and technological unfamiliarity among some pet owners, early adopters signal strong future potential.
These tech-enhanced products offer a glimpse into a future where pet entertainment becomes integrated with broader wellness tracking—bridging the gap between consumer electronics and animal care.
Regulatory, Safety, and Environmental Impediments
Safety regulation is an ever-present concern. Pet toys must meet rigorous standards for durability, non-toxicity, and design integrity to prevent choking or ingestion hazards. However, standards are not uniformly enforced across regions, complicating cross-border distribution strategies.
Environmental concerns are also mounting. The push for biodegradable or recyclable toys is hampered by higher production costs and limited material availability. Brands seeking to differentiate themselves on eco-credentials must invest heavily in research and supply chain reconfiguration.
Conclusion
The pet toys market operates at the intersection of behavioral science, industrial production, and shifting cultural values. As pets occupy increasingly central roles in human life, the demand for intelligent, safe, and ethically produced toys is unlikely to abate. The sector’s resilience lies in its adaptability—its willingness to integrate technology, respond to consumer ethics, and prioritize the functional over the frivolous. The future of pet toys is neither playful nor perfunctory—it is strategic.