Report Overview:
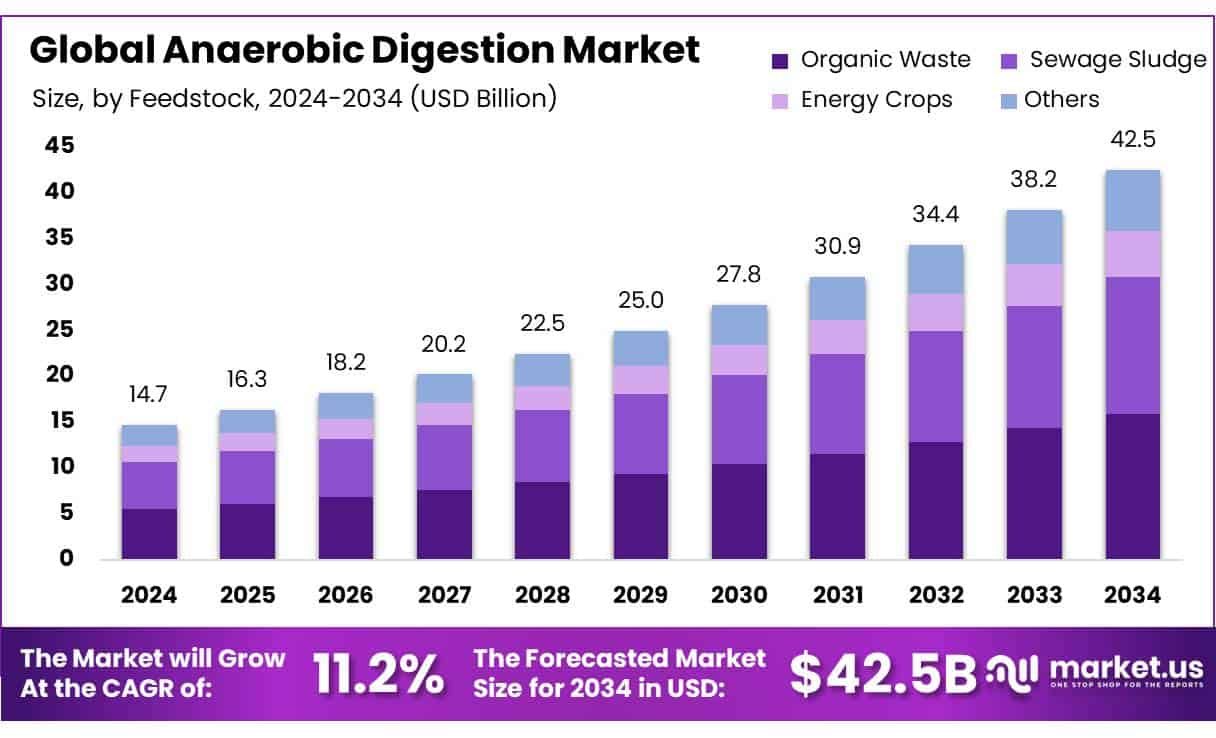
The global anaerobic digestion market is gaining momentum as countries and industries increasingly seek greener, more sustainable solutions for waste and energy. As of 2024, the market is valued at USD 14.7 billion, and it’s expected to nearly triple to USD 42.5 billion by 2034, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.2%.This strong growth is underpinned by mounting environmental concerns, supportive government policies, and growing interest in circular economy practices.
AD technology converts organic waste such as agricultural refuse, food scraps, sewage sludge, and energy crops into biogas and nutrient-rich digestate. Biogas can be used to generate electricity, heating, or biomethane, while digestate serves as a valuable fertilizer.The result is a powerful combination of process efficiency, cost effectiveness, and tangible environmental benefits, such as lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced landfill usage.
North America currently leads the market, holding approximately 43.7% of total revenue, with strong uptake across the U.S. agricultural, municipal, and waste management sectors . Globally, technologies like Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) dominate product offerings, while wet AD processes account for around 65% of operations.
Key Takeaways:
The global anaerobic digestion market was valued at USD 14.7 billion in 2024.
The global anaerobic digestion market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.20% and is estimated to reach USD 42.5 billion by 2034.
Among feedstock, organic waste accounted for the largest market share of 37.5%.
Among product types, Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) accounted for the majority of the market share at 43.3%.
By process, Wet AD accounted for the largest market share of 65.3%.
By end use, waste management and treatment accounted for the majority of the market share at 38.4%.
North America is estimated as the largest market for anaerobic digestion with a share of 43.7% of the market share.
Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/global-anaerobic-digestion-market/free-sample/
Key Market Segments:
By Feedstock
Organic Waste
Sewage Sludge
Energy Crops
Others
By Product Type
Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
Internal Circulation Reactor (IC Reactor)
Expanded Granular Sludge Bed Digestion (EGSB)
By Process
Wet AD
Dry AD
By End-Use
Waste Management and Treatment
Energy Generation
Agriculture
Others
Drivers:
The anaerobic digestion (AD) market is primarily driven by the global demand for sustainable and eco-friendly waste management solutions. Governments, municipalities, and industries are under increasing pressure to reduce landfill dependency, cut greenhouse gas emissions, and comply with climate-related regulations. Anaerobic digestion, by converting organic waste into renewable energy and biofertilizers, offers a viable solution to tackle all three.
As landfills fill up and environmental penalties rise, AD stands out for its dual ability to manage waste and generate biogas making it a strategic technology aligned with global sustainability goals. Countries with national carbon neutrality targets are especially encouraging investment in this sector, seeing AD as a critical component in their decarbonization roadmaps.
Another major driver is the growing emphasis on circular economy models. The anaerobic digestion process doesn’t just reduce waste it transforms it into usable resources such as biogas for electricity or heat and digestate for agricultural use. This closed-loop model appeals to industries looking to reduce waste output, recover energy, and minimize environmental footprints.
For example, the food and beverage industry can redirect organic by-products into AD plants rather than sending them to incinerators or landfills. This not only meets regulatory obligations but also enhances corporate sustainability branding and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) ratings, which are increasingly scrutinized by investors and customers alike.
Opportunities:
A significant opportunity lies in the global shift toward biomethane as a clean fuel alternative. While traditional biogas is typically used on-site, upgrading it to biomethane opens new commercial avenues. Biomethane can be fed directly into existing natural gas pipelines, used to power CNG vehicles, or sold as renewable fuel for industrial applications.
As countries move toward cleaner transportation fuels and reduce reliance on fossil-based natural gas, the demand for biomethane is expected to surge. This creates an opportunity for AD facility owners to invest in gas upgrading technologies and tap into higher-value energy markets, particularly in Europe and North America where biomethane integration policies are strengthening.
Another emerging opportunity is in digestate valorization. The solid and liquid byproducts of the anaerobic digestion process, once seen as waste, are now being repurposed as valuable biofertilizers, soil amendments, and organic conditioners. As the global agriculture sector increasingly focuses on organic and sustainable farming, digestate is gaining traction as an eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers.
Countries with phosphate-scarce soils are especially interested in these nutrient-rich outputs. Additionally, with ongoing research into digestate refinement, there is potential for creating even higher-value products such as pelletized fertilizers or compost blends, which can be packaged and sold commercially.
Restraints:
Despite its promise, the anaerobic digestion market faces significant economic risks, particularly the high upfront capital costs associated with setting up new facilities. Building an AD plant involves investments in civil infrastructure, mechanical equipment, gas purification units, safety systems, and post-treatment facilities for digestate. These costs can be burdensome for small farms, rural communities, or municipalities operating under budget constraints.
Without consistent government subsidies, favorable tariffs, or public-private partnerships, many projects may struggle to reach financial viability. Furthermore, long payback periods can deter investors, especially in markets with cheaper or more established energy alternatives.
There are also technical risks related to operational complexity and feedstock variability. Anaerobic digestion is a sensitive biological process that depends on maintaining precise temperature, pH, and microbial conditions. Variations in feedstock composition such as shifts in moisture content, contamination, or nutrient imbalance can disrupt the microbial ecosystem within the digester. This can result in reduced biogas output or even total process failure.
Additionally, the use of non-organic waste or chemically treated materials can harm the bacteria critical to digestion. Operators must be trained, and systems must be monitored regularly, requiring ongoing technical expertise that isn’t always available in all regions.
Trends:
One of the most influential trends in the anaerobic digestion market is the transition from centralized to decentralized systems. Smaller, localized digesters are gaining popularity because they allow waste to be treated where it’s produced. Whether installed on farms, at food processing plants, or near municipal facilities, these systems help reduce transportation emissions and improve energy resilience.
Decentralized models are especially valuable in disaster-prone or remote regions where central grid connectivity is unreliable. These systems are now more affordable, thanks to prefabricated units and containerized digesters, making them suitable for both developed and developing countries.
Another fast-growing trend is biogas upgrading to produce biomethane. While basic AD systems traditionally produced biogas for local use, the market is shifting toward purification technologies that remove impurities and boost methane content to pipeline standards.
Techniques like membrane separation, water scrubbing, and pressure swing adsorption are becoming more common, driven by rising demand for renewable natural gas (RNG). Biomethane is increasingly being used in public transport fleets, heating networks, and industrial applications. As more gas utilities integrate RNG into their supply, this trend is expected to become a central growth engine for the AD market.
Market Key Players:
Adnams plc
Clarke Energy
WELTEC BIOPOWER GMBH
Schneider Electric
EnviTec Biogas AG
Northern Biogas
Bioenergy Devco
AAT Abwasser- und Abfalltechnik GmbH
Viessmann Climate Solutions SE
Agrinz Technologies GmbH
PlanET Biogastechnik GmbH
Agraferm GmbH
Scandinavian Biogas Fuels International AB
BDI-BioEnergy International GmbH
Gasum Oy
Nature Energy
ENGIE Group
AB HOLDING SPA
Capstone Green Energy Corporation
Compact Membrane System
Others
Conclusion:
In essence, the anaerobic digestion market is at an exciting inflection point. Its deep roots in sustainable waste treatment are now intersecting with expanding roles in clean energy generation. As countries worldwide elevate their climate targets and seek energy independence, AD systems offer a compelling two-for-one solution: efficient organic waste disposal and renewable energy output.
To capture this potential, stakeholders must address technical challenges with consistent feedstock, optimized microbial conditions, and flexible infrastructure. Policy alignment and financial mechanisms will also be essential to de-risk investment. Ultimately, AD isn’t just a green niche it’s evolving into a core pillar of a sustainable waste to‑energy landscape, with rippling benefits for climate, communities, and circular economies.